Operation
The water pump (also called a coolant pump) is driven by one of two methods.
- Crankshaft belt
- Camshaft
Coolant recirculates from the radiator to the engine and back to the radiator. Low-temperature coolant leaves the radiator by the bottom outlet. It is pumped into the warm engine block, where it picks up some heat. From the block, the warm coolant flows to the hot cylinder head, where it picks up more heat.
- NOTE: Some engines use reverse cooling. This means that the coolant flows from the radiator to the cylinder head(s) before flowing to the engine block.

A demonstration engine running on a stand showing the amount of coolant flow that actually occurs through the cooling system.
Frequently Asked Quesiton: How much Coolant Can a Water Pump Move?
A typical water pump can move a maximum of about 7,500 gallons (28,000 liters) of coolant per hour, or recirculate the coolant in the engine over 20 times per minute. This means that a water pump could be used to empty a typical private swimming pool in an hour! The slower the engine speed, the less power is consumed by the water pump. However, even at 35 mph (56 km/h), the typical water pump still moves about 2,000 gallons (7,500 liters) per hour or 0.5 gallon (2 liters) per second!
Water pumps are not positive displacement pumps. The water pump is a centrifugal pump that can move a large volume of coolant without increasing the pressure of the coolant. The pump pulls coolant in at the center of the impeller. Centrifugal force throws the coolant outward so that it is discharged at the impeller tips.
As engine speeds increase, more heat is produced by the engine and more cooling capacity is required. The pump impeller speed increases as the engine speed increases to provide extra coolant flow at the very time it is needed.
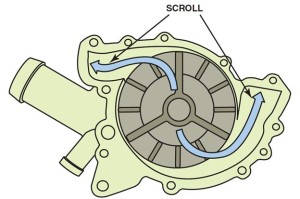
Coolant leaving the pump impeller is fed through a scroll. The scroll is a smoothly curved passage that changes the fluid flow direction with minimum loss in velocity. The scroll is connected to the front of the engine so as to direct the coolant into the engine block. On V-type engines, two outlets are often used, one for each cylinder bank. Occasionally, diverters are necessary in the water pump scroll to equalize coolant flow between the cylinder banks of a V-type engine in order to equalize the cooling.
Water Pump Service
A worn impeller on a water pump can reduce the amount of coolant flow through the engine.
If the seal of the water pump fails, coolant will leak out of the weep hole. The hole allows coolant to escape without getting trapped and forced into the water pump bearing assembly.
The hole allows coolant to escape without getting trapped and forced into the water pump bearing assembly.
If the bearing is defective, the pump will usually be noisy and will have to be replaced. Before replacing a water pump that has failed because of a loose or noisy bearing, check all of the following:
- Drive belt tension
- Bent fan
- Fan for balance
If the water pump drive belt is too tight, excessive force may be exerted against the pump bearing. If the cooling fan is bent or out of balance, the resulting vibration can damage the water pump bearing.
Tech Tip: Release the Belt Tension before Checking a Water Pump
The technician should release water pump belt tension before checking for water pump bearing looseness. To test a water pump bearing, it is normal to check the fan for movement; however, if the drive belt is tight, any looseness in the bearing will not be felt.
Next Steps towards ASE Certification
Now that you’re familiar with Water Pumps in Automotive Engine Coolant Systems, try out our free Automotive Service Excellence Tests to see how much you know!
![ASE Certification Training HQ - Free ASE Practice Tests [Updated 2021]](https://asecertificationtraining.com/wp-content/themes/simplefolio/images/ASE Certification Logo.png)