Catalyst Purpose and Function
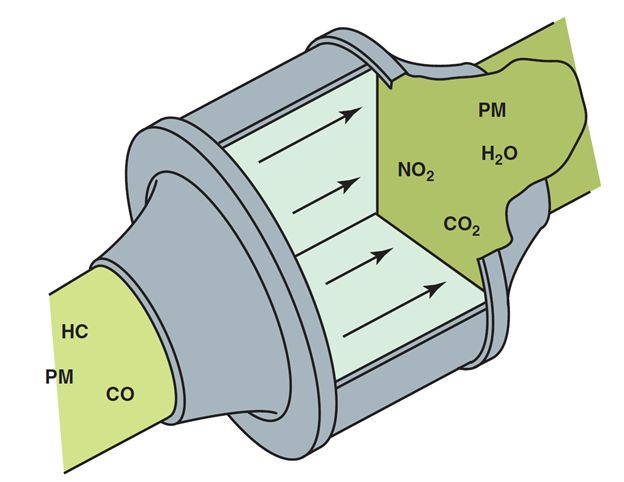
Diesel oxidation catalysts (DOC) are used in all light-duty diesel engines, since 2007. They consist of a flow-through honeycomb-style substrate structure that is wash coated with a layer of catalyst materials, similar to those used in a gasoline engine catalytic converter. These materials include the precious metals platinum and palladium, as well as other base metal catalysts.
Catalysts chemically react with exhaust gas to convert harmful nitrogen oxide into nitrogen dioxide, and to oxidize absorbed hydrocarbons. The chemical reaction acts as a combustor for the unburned fuel that is characteristic of diesel compression ignition. The main function of the DOC is to start a regeneration event by converting the fuel-rich exhaust gases to heat.
The DOC also reduces:
- Carbon monoxide (CO)
- Hydrocarbons (HC)
Odor-causing compounds such as aldehydes and sulfur
Next Steps towards ASE Certification
Now that you’re familiar with Diesel Engine Catalysts, try out our free Automotive Service Excellence Tests to see how much you know!
![ASE Certification Training HQ - Free ASE Practice Tests [Updated 2021]](https://asecertificationtraining.com/wp-content/themes/simplefolio/images/ASE Certification Logo.png)