Turbocharged Diesels
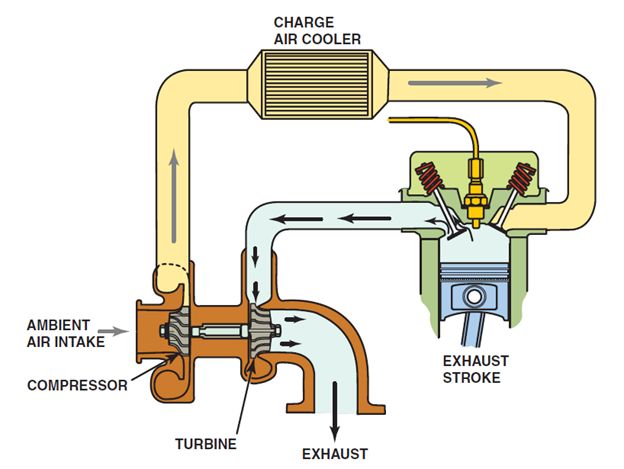
A turbocharger greatly increases engine power by pumping additional compressed air into the combustion chambers. This allows a greater quantity of fuel to be burned in the cylinders resulting in greater power output. In a turbocharger, the turbine wheel spins as exhaust gas flows out of the engine and drives the turbine blades. The turbine spins the compressor wheel at the opposite end of the turbine shaft, pumping air into the intake system.
Air Charge Cooler
The first component in a typical turbocharger system is an air filter through which ambient air passes before entering the compressor. The air is compressed, which raises its density (mass/unit volume). All currently produced light-duty diesels use an air charge cooler whose purpose is to cool the compressed air to further raise the air density. Cooler air entering the engine means more power can be produced by the engine.
Next Steps towards ASE Certification
Now that you’re familiar with Diesel Engine Turbochargers, try out our free Automotive Service Excellence Tests to see how much you know!
![ASE Certification Training HQ - Free ASE Practice Tests [Updated 2021]](https://asecertificationtraining.com/wp-content/themes/simplefolio/images/ASE Certification Logo.png)